A typical refrigerator requires 100 to 800 watts to run on a generator. The exact wattage depends on the refrigerator model.

Running a refrigerator on a generator is essential during power outages. Understanding the wattage needs ensures you choose the right generator. Most modern refrigerators use around 100 to 800 watts, but older models may need more power. It’s essential to check the specific requirements of your fridge.
This helps avoid overloading your generator, ensuring efficient performance. Knowing the wattage also aids in managing other appliances simultaneously. Always consult your refrigerator’s manual for precise details. Proper preparation keeps your food safe and your generator running smoothly.
Understanding Wattage
Understanding wattage helps you run your fridge on a generator. It ensures your fridge gets the right power. Knowing wattage prevents overloading your generator.
What Is Wattage?
Wattage measures electrical power. It shows how much energy a device uses. Watts (W) is the unit used to measure wattage. A higher wattage means more power use.
Every appliance has a specific wattage. Check your fridge’s label to find its wattage. This helps you choose a suitable generator.
Wattage Vs. Voltage
Voltage measures electrical potential difference. It is different from wattage. Voltage is measured in volts (V). It would be best if you had both wattage and voltage to understand your fridge’s power needs.
Here is a simple table to explain the difference:
| Term | Unit | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Wattage | Watts (W) | Measures power usage |
| Voltage | Volts (V) | Measures electrical potential |
To find the wattage of your fridge, multiply voltage by current (amps). Here’s a formula:
Wattage (W) = Voltage (V) x Current (A)
For example, a fridge using 120V and 5A needs 600W.

Credit: www.bigrentz.com
Fridge Power Requirements
Understanding the power requirements of your fridge is crucial. It helps to run it efficiently on a generator. Knowing the exact wattage needed can prevent overloading. This section delves into typical wattage and factors affecting power usage.
Typical Wattage For Fridges
Fridges vary in size and type. Their power usage can differ significantly. Here’s a table showing the typical wattage for common fridge types.
| Fridge Type | Running Wattage | Starting Wattage |
|---|---|---|
| Mini Fridge | 50-100 Watts | 150 Watts |
| Standard Fridge (Top Freezer) | 150-200 Watts | 600-700 Watts |
| Side-by-Side Fridge | 400-500 Watts | 800-1200 Watts |
| French Door Fridge | 500-700 Watts | 1000-2000 Watts |
Factors Affecting Power Usage
Several factors can affect a fridge’s power usage. Here are some key points to consider:
- Size: Larger fridges need more power.
- Age: Older fridges use more electricity.
- Insulation: Poor insulation increases power usage.
- Temperature Settings: Lower settings consume more power.
- Frequency of Use: Frequent opening uses more energy.
By understanding these factors, you can better estimate your fridge’s power needs. This ensures your generator can handle the load.
Choosing The Right Generator
Finding the right generator for your fridge is essential. Your fridge needs a steady power supply. Not all generators are the same. Some work better for fridges than others. Let’s look at the types of generators and critical features to consider.
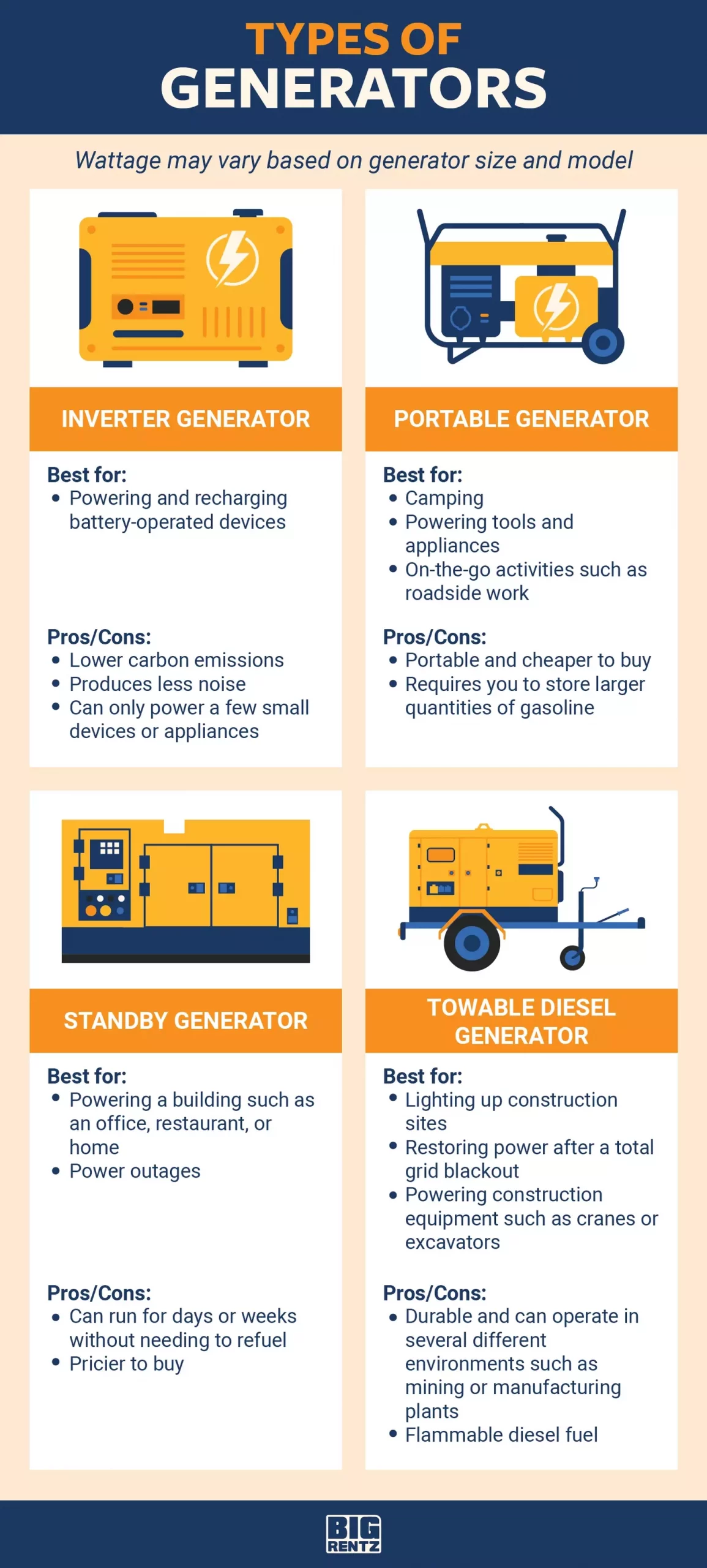
Types Of Generators
There are different types of generators. Here are the most common ones:
- Portable Generators: Easy to move and use. Suitable for short power outages.
- Inverter Generators: Provide clean and stable power. It is ideal for sensitive electronics and appliances.
- Standby Generators: Installed permanently. Automatically turn on during power outages. Best for long-term use.
Key Features To Consider
When choosing a generator, consider these features:
- Wattage: Make sure the generator can handle your fridge’s power needs. Check your fridge’s wattage and choose a generator with enough capacity.
- Fuel Type: Generators use different fuels like gasoline, propane, or diesel. Choose one that is easy for you to get and store.
- Run Time: Check how long the generator can run on a full tank. Longer run times mean less frequent refueling.
- Noise Level: Some generators are noisy. Look for models with lower decibel ratings for quieter operation.
- Portability: If you need to move the generator often, choose a lighter, portable model.
| Feature | Portable Generators | Inverter Generators | Standby Generators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wattage | Varies, check specs | Varies; check specs | Varies; check specs |
| Fuel Type | Gasoline, propane | Gasoline, propane | Natural gas, propane |
| Run Time | Short to medium | Medium to long | Very long |
| Noise Level | Moderate | Low | Low to moderate |
| Portability | High | High | Low |
Choosing the right generator ensures your fridge runs smoothly. Remember to match the generator’s capacity with your fridge’s needs. This keeps your food safe and fresh during power outages.
Calculating Power Needs
Understanding how many watts your fridge uses is critical. This helps you choose the right generator. Calculating power needs ensures your fridge runs smoothly during power outages.
Step-by-step Calculation
Follow these steps to calculate your fridge’s power needs:
- Find the fridge’s wattage on its label.
- Check the starting watts and running watts. Starting watts are higher.
- Calculate the total wattage needed. Add 20% to running watts for safety.
For example:
| Fridge Wattage | Starting Watts | Running Watts | Total Watts Needed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 700W | 2200W | 700W | 840W |
Additional Appliances To Consider
Your generator might power more than just the fridge. Consider other essential appliances:
- Lights
- Microwave
- Television
- Fans
List their wattages and sum them up. Ensure your generator can handle the load.
Safety Precautions
Running your fridge on a generator requires careful attention to safety. Ensuring proper setup and avoiding overloads is crucial. Follow these safety tips to protect your appliances and yourself.
Proper Setup
Start by setting up the generator in a safe location. Place it outside to prevent carbon monoxide buildup. Please keep it away from windows, doors, and vents. Make sure the area is dry and free of debris.
Use a heavy-duty extension cord rated for outdoor use. Ensure the cord is in good condition with no cuts or frays. Connect the cord to the generator first, then to the fridge.
Check the generator’s wattage rating before powering the fridge. The generator should provide more watts than the fridge requires. Most fridges need between 600 to 800 watts to run.
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for starting and operating the generator. Turn off all appliances before starting the generator. Once the generator is running smoothly, turn on the fridge.
Avoiding Overloads
Overloading a generator can cause damage to both the generator and the fridge. Calculate the total wattage of all devices you plan to run to avoid this. Ensure the total wattage does not exceed 80% of the generator’s capacity.
Use a wattage calculator or refer to the appliance labels for accurate measurements. If the fridge requires 700 watts, and the generator is 1000 watts, avoid adding more than 100 watts of load.
Monitor the generator while it’s running. If it shows signs of strain, disconnect some devices. Signs of overload include flickering lights, unusual noises, or the generator shutting down unexpectedly.
Keep the generator well-maintained. Regularly check oil levels, air filters, and spark plugs. Proper maintenance ensures the generator runs efficiently and safely.
| Appliance | Average Wattage |
|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 600-800 watts |
| Microwave | 1000 watts |
| Coffee Maker | 900 watts |
| Television | 100-200 watts |
These steps ensure a safe and efficient setup for running your fridge on a generator. Prioritize safety to protect your home and appliances.
Maintaining Your Generator
Maintaining your generator is crucial for its longevity and efficiency. A well-maintained generator ensures your fridge runs smoothly during power outages. Follow these tips to keep your generator in top shape.
Routine Maintenance
Routine maintenance involves regular checks and servicing. Here are some critical steps:
- Check oil levels: Keep oil levels within the recommended range.
- Inspect filters: Clean or replace air and fuel filters regularly.
- Examine spark plugs: Replace spark plugs if worn out.
- Run the generator: Operate the generator for at least 30 minutes monthly.
- Store properly: Keep the generator in a dry, cool place.
Following these steps ensures your generator runs efficiently.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Generators may face common issues. Here are solutions to some of them:
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Generator won’t start | Check fuel, oil levels, and battery connections. |
| Low power output | Inspect air filter and clean or replace it. |
| Overheating | Ensure proper ventilation and check coolant levels. |
| Strange noises | Check for loose parts and tighten them. |
Addressing these issues promptly keeps your generator reliable.
Cost Considerations
Understanding the cost considerations of running your fridge on a generator is crucial. It would be best to account for both the initial investment and the long-term costs. Making an informed decision ensures you get the best value for your money.
Initial Investment
The initial investment includes the cost of the generator and any necessary accessories. Here’s a breakdown:
- Generator Cost: Prices vary based on wattage and brand. A reliable generator for a fridge may cost between $300 and $1,000.
- Accessories: Extension cords, fuel cans, and stabilizers. These can add another $50 to $100.
Investing in a high-quality generator ensures better performance and longevity.
Long-term Costs
Long-term costs include fuel, maintenance, and potential repairs. Here’s what you need to consider:
| Expense Type | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Fuel: Gasoline or propane | $50-$100 per month |
| Maintenance: Oil changes, filters | $20-$50 per year |
| Repairs: Unexpected issues | $50-$200 per year |
Maintaining your generator properly can reduce long-term costs. Regular checks and timely repairs can prevent more significant issues. Using high-quality fuel and parts also helps.
Credit: www.quora.com
Credit: www.bigrentz.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Big a Generator Do I Need to Run a Refrigerator?
A 2,000-watt generator is typically sufficient to run a refrigerator. Check your refrigerator’s wattage for exact requirements.
Can A 2500 Watt Generator Run A Refrigerator?
Yes, a 2500-watt generator can run a refrigerator. Most refrigerators need around 1200-2000 watts to start.
Will a 1000w Generator Run a Refrigerator?
Yes, a 1000W generator can run a refrigerator. Ensure the fridge’s starting wattage doesn’t exceed the generator’s capacity.
Can a 1800 Watt Generator Run a Refrigerator?
Yes, an 1800-watt generator can run a refrigerator. Ensure the fridge’s starting wattage is within the generator’s capacity.
Conclusion
Understanding your fridge’s wattage ensures efficient generator use. Always check your appliance specifications. Proper planning prevents power issues. Running your fridge on a generator can be simple and stress-free. Stay informed and enjoy uninterrupted cooling.


GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings